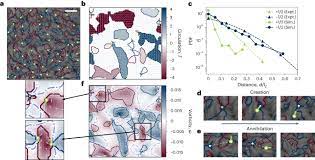
 Active processes drive biological dynamics across various scales and include subcellular cytoskeletal remodelling, tissue development in embryogenesis and the population-level expansion of bacterial colonies. In each of these, biological functionality requires collective flows to occur while self-organised structures are protected. However, the mechanisms by which active flows can spontaneously constrain their dynamics to preserve structure are not known. Here, by studying collective flows and defect dynamics in active nematic films, we demonstrate the existence of a self-constraint, namely a two-way, spontaneously arising relationship between activity-driven isosurfaces of flow boundaries and mesoscale nematic structures. We show that self-motile defects are tightly constrained to viscometric surfaces, which are contours along which the vorticity and the strain rate are balanced. This in turn reveals that self-motile defects break mirror symmetry when they move along a single viscometric surface. This is explained by an interdependence between viscometric surfaces and bend walls, which are elongated narrow kinks in the orientation field. These findings indicate that defects cannot be treated as solitary points. Instead, their associated mesoscale deformations are key to the steady-state coupling to hydrodynamic flows. This mesoscale cross-field self-constraint offers a framework for tackling complex three-dimensional active turbulence, designing dynamic control into biomimetic materials and understanding how biological systems can employ active stress for dynamic self-organisation.
Active processes drive biological dynamics across various scales and include subcellular cytoskeletal remodelling, tissue development in embryogenesis and the population-level expansion of bacterial colonies. In each of these, biological functionality requires collective flows to occur while self-organised structures are protected. However, the mechanisms by which active flows can spontaneously constrain their dynamics to preserve structure are not known. Here, by studying collective flows and defect dynamics in active nematic films, we demonstrate the existence of a self-constraint, namely a two-way, spontaneously arising relationship between activity-driven isosurfaces of flow boundaries and mesoscale nematic structures. We show that self-motile defects are tightly constrained to viscometric surfaces, which are contours along which the vorticity and the strain rate are balanced. This in turn reveals that self-motile defects break mirror symmetry when they move along a single viscometric surface. This is explained by an interdependence between viscometric surfaces and bend walls, which are elongated narrow kinks in the orientation field. These findings indicate that defects cannot be treated as solitary points. Instead, their associated mesoscale deformations are key to the steady-state coupling to hydrodynamic flows. This mesoscale cross-field self-constraint offers a framework for tackling complex three-dimensional active turbulence, designing dynamic control into biomimetic materials and understanding how biological systems can employ active stress for dynamic self-organisation.
NATURE PHYSICS
By: Louise C. Head, Claire Doré, Ryan R. Keogh, Lasse Bonn, Giuseppe Negro, Davide Marenduzzo, Amin Doostmohammadi, Kristian Thijssen, Teresa López-León, Tyler N. Shendruk.
Nature Physics volume 20, pages 492–500 (2024)
DOI: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41...

