A new study from Daeseok Kim and Teresa Lopez-Leon of Gulliver lab, in collaboration with Helen Ansell, Randall Kamien, and Eleni Katifori of the University of Pennsylvania, describes how polymer spheres can transform into twisted spindles thanks to insights from 16th century navigation tools. A combination of experimental and theoretical efforts shows how loxodromes, or rhumb lines, can form from polymer spheres, resulting in complex patterns that are ten times smaller than the width of a human hair.
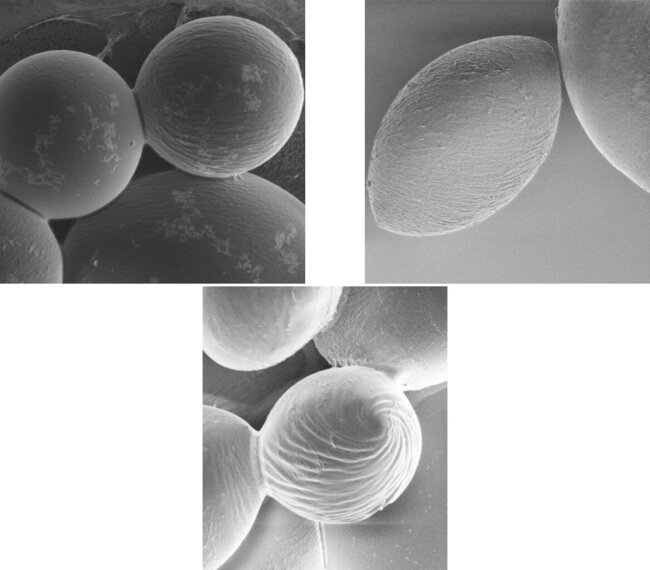
Scanning electron microscope images showing polymers in a spherical configuration (left); when a new solvent is added, the spheres twist and change into elongated twisted spindles (right). At the top of the spindles (bottom) are one micron spirals. (Image: Daeseok Kim)

