Publications
-
Trading particle shape with fluid symmetry: on the mobility matrix in 3-D chiral fluids
Chiral fluids – such as fluids under rotation or a magnetic field as well as synthetic and biological active fluids – flow in a different way than ordinary ones. Due to symmetries broken at the microscopic level, chiral fluids may have (...)
-
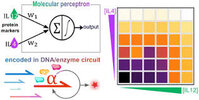
DNA circuit-based immunoassay for ultrasensitive protein pattern classification
Cytokines are important immune modulators, and pivotal biomarkers for the diagnostic of various diseases. In standard analytical procedure, each protein is detected individually, using for instance gold standard ELISA protocols or nucleic acid (...)
-
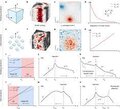
Pattern formation by turbulent cascades
Fully developed turbulence is a universal and scale-invariant chaotic state characterized by an energy cascade from large to small scales at which the cascade is eventually arrested by dissipation1,2,3,4,5,6. Here we show how to harness these (...)
-
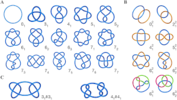
Topology in soft and biological matter
The last years have witnessed remarkable advances in our understanding of the emergence and consequences of topological constraints in biological and soft matter. Examples are abundant in relation to (bio)polymeric systems and range from the (...)
-
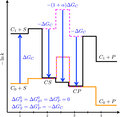
A role for conformational changes in enzyme catalysis
The role played by conformational changes in enzyme catalysis is controversial. In addition to examining specific enzymes, studying formal models can help identify the conditions under which conformational changes promote catalysis. Here, we (...)
-
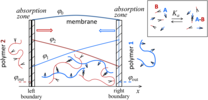
Growth of membranes formed by associating polymers at interfaces
Polymer association at liquid–liquid interfaces is a promising way to spontaneously obtain soft self-healing membranes. In the case of reversible bonding between two polymers, the macromolecules are mobile everywhere within the membrane and (...)
-
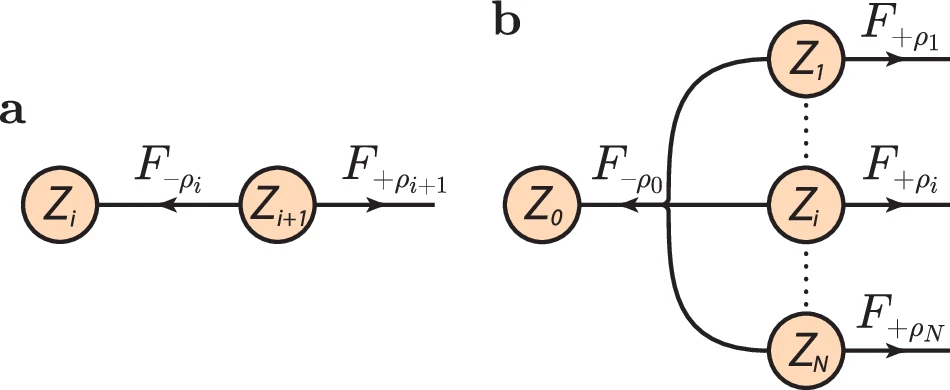
Structural constraints limit the regime of optimal flux in autocatalytic reaction networks
Autocatalytic chemical networks play a predominant role in a large number of natural systems such as in metabolic pathways and in ecological networks. Despite recent efforts, the precise impact of thermodynamic constraints on these networks (...)
-

Spontaneous self-constraint in active nematic flows
Active processes drive biological dynamics across various scales and include subcellular cytoskeletal remodelling, tissue development in embryogenesis and the population-level expansion of bacterial colonies. In each of these, biological (...)
-
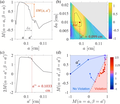
Static Bell test in pilot-wave hydrodynamics
Since its discovery in 2005, the hydrodynamic pilot-wave system has provided a concrete macroscopic realization of wave-particle duality and concomitant classical analogs of a growing number of quantum effects. The question naturally arises as (...)
-
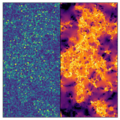
Dynamical Facilitation Governs the Equilibration Dynamics of Glasses
Convincing evidence of domain growth in the heating of ultrastable glasses suggests that the equilibration dynamics of supercooled liquids could be driven by a nucleation and growth mechanism. We investigate this possibility by simulating the (...)


