Publications
-
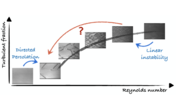
Laminar-Turbulent Patterns in Shear Flows: Evasion of Tipping, Saddle-Loop Bifurcation, and Log Scaling of the Turbulent Fraction
Spatial pattern formation can be a signal for tipping points and abrupt transitions in complex systems. In wall shear flows, the homogeneous turbulent state is disconnected from the laminar one and disappears in a tipping catastrophe scenario. (...)
-
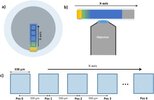
Probing the colloidal behavior of a cell wall polysaccharides-degrading enzyme in a highly constrained model system
Understanding the specific interaction of cell wall polysaccharides degrading-enzymes with their substrates is of fundamental and practical interest for the fine grasp of their activity. Such interactions are difficult to unveil in real-life (...)
-
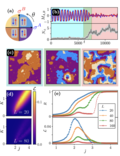
Nonreciprocal Ising model
Systems with nonreciprocal interactions generically display time-dependent states. These are routinely observed in finite systems, from neuroscience to active matter, in which globally ordered oscillations exist. However, the stability of these (...)
-
Martingale drift of Langevin dynamics and classical canonical spin statistics. II.
In the previous paper we have shown analytically that the drift function of the 𝑑-dimensional Langevin equation is the Langevin function with a properly chosen scale factor when the evolution of the drift function is a martingale associated (...)
-

What does an ion feel at the electrochemical interface? Revisiting electrosorption through nonlocal electrostatics
The traditional Gouy–Chapman–Stern theory has been effective in explaining the behavior of dilute electrolytes in the electrical double layer but falls short when it comes to describing how ions behave at the metal/electrolyte interface. This (...)
-
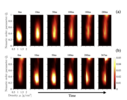
Dynamic Heterogeneity of Short Semi-crystalline Polymer Chains during Recrystallization
The instant crystallization of semi-crystalline polymers have become possible following the recent advances in Fast Scanning Calorimetry (FSC) and enables to make a bridge between the time scale available experimentally with those accessible (...)
-
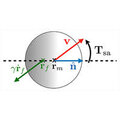
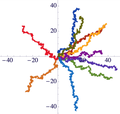
Self-aligning polar active matter
Self-alignment describes the property of a polar active unit to align or antialign its orientation toward its velocity. In contrast to mutual alignment, where the headings of multiple active units tend to directly align with each other—as in (...)
-
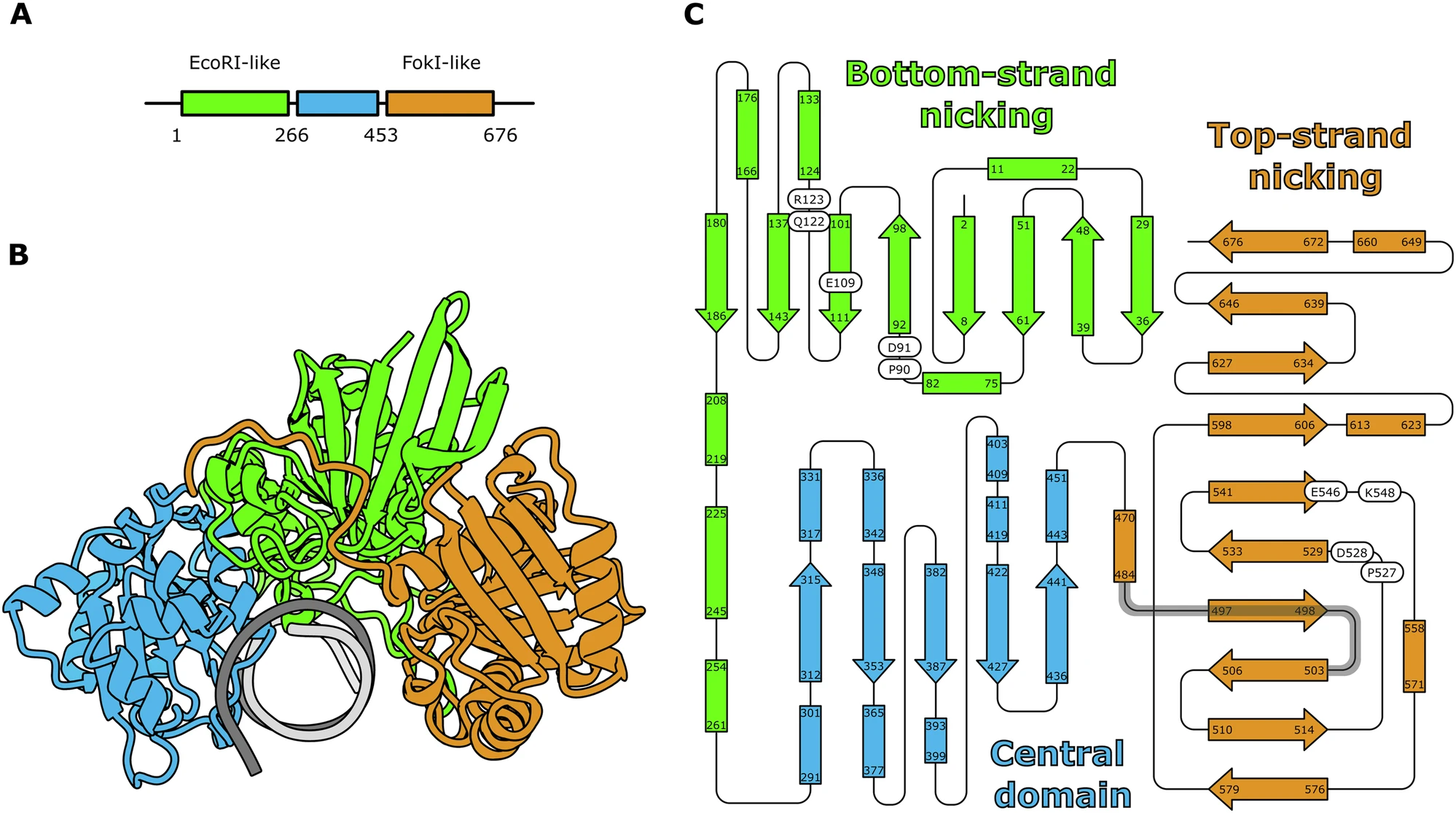
Crystal structures of monomeric BsmI restriction endonuclease reveal coordinated sequential cleavage of two DNA strands
BsmI, a thermophilic Type IIS restriction endonuclease from Bacillus stearothermophilus, presents a unique structural composition, housing two distinct active sites within a single monomer. Recognition of the non-symmetrical 5’-GAATGC-3’ (...)
-
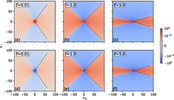
Stationary and transient correlations in driven electrolytes
Particle–particle correlation functions in ionic systems control many of their macroscopic properties. In this work, we use stochastic density functional theory to compute these correlations, and then we analyze their long-range behavior. In (...)
-
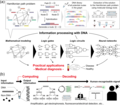
Harnessing DNA computing and nanopore decoding for practical applications: from informatics to microRNA-targeting diagnostics
DNA computing represents a subfield of molecular computing with the potential to become a significant area of next-generation computation due to the high programmability inherent in the sequence-dependent molecular behaviour of DNA. Recent (...)


