Publications
-
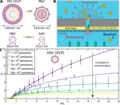
Soft jamming of viral particles in nanopores
Viruses have remarkable physical properties and complex interactions with their environment. However, their aggregation in confined spaces remains unexplored, although this phenomenon is of paramount importance for understanding viral (...)
-
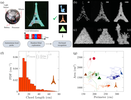
Frugal random exploration strategy for shape recognition using statistical geometry
Very distinct strategies can be deployed to recognize and characterize an unknown environment or a shape. A recent and promising approach, especially in robotics, is to reduce the complexity of the exploratory units to a minimum. Here, we show (...)
-
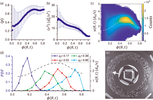
Traveling fronts in vibrated polar disks: At the crossroad between polar ordering and jamming
We investigate experimentally the collective motion of polar vibrated disks in an annular geometry, varying both the packing fraction and the amplitude of the angular noise. For low enough noise and large enough density, an overall collective (...)
-
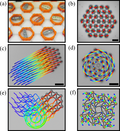
Model of Active Solids: Rigid Body Motion and Shape-Changing Mechanisms
Active solids such as cell collectives, colloidal clusters, and active metamaterials exhibit diverse collective phenomena, ranging from rigid body motion to shape-changing mechanisms. The nonlinear dynamics of such active materials remains, (...)
-
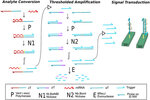
Time-encoded electrical detection of trace RNA biomarker by integrating programmable molecular amplifier on chip
One of the serious challenges facing modern point-of-care (PoC) molecular diagnostic platforms relate to reliable detection of low concentration biomarkers such as nucleic acids or proteins in biological samples. Non-specific analyte-receptor (...)
-
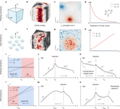
Pattern formation by turbulent cascades
Fully developed turbulence is a universal and scale-invariant chaotic state characterized by an energy cascade from large to small scales at which the cascade is eventually arrested by dissipation1,2,3,4,5,6. Here we show how to harness these (...)
-
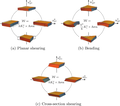
Odd elasticity and topological waves in active surfaces
Odd elasticity describes active elastic systems whose stress-strain relationship is not compatible with a potential energy. As the requirement of energy conservation is lifted from linear elasticity, new antisymmetric (odd) components appear in (...)
-
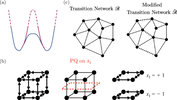
Interplay between Markovianity and progressive quenching
Progressive quenching (PQ) is a process in which we sequentially fix a system’s degrees of freedom, which would otherwise evolve according to their stochastic dynamics. Previous studies have discovered what we refer to as the hidden martingale (...)
-

Functional analysis of single enzymes combining programmable molecular circuits with droplet-based microfluidics
The analysis of proteins at the single-molecule level reveals heterogeneous behaviours that are masked in ensemble-averaged techniques. The digital quantification of enzymes traditionally involves the observation and counting of single (...)
-
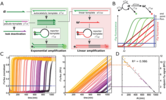
Coupling Exponential to Linear Amplification for Endpoint Quantitative Analysis
Exponential DNA amplification techniques are fundamental in ultrasensitive molecular diagnostics. These systems offer a wide dynamic range, but the quantification requires real-time monitoring of the amplification reaction. Linear amplification (...)


